-
Use the Add Data button to add each of the datasets you wish to convert to the map document.

-
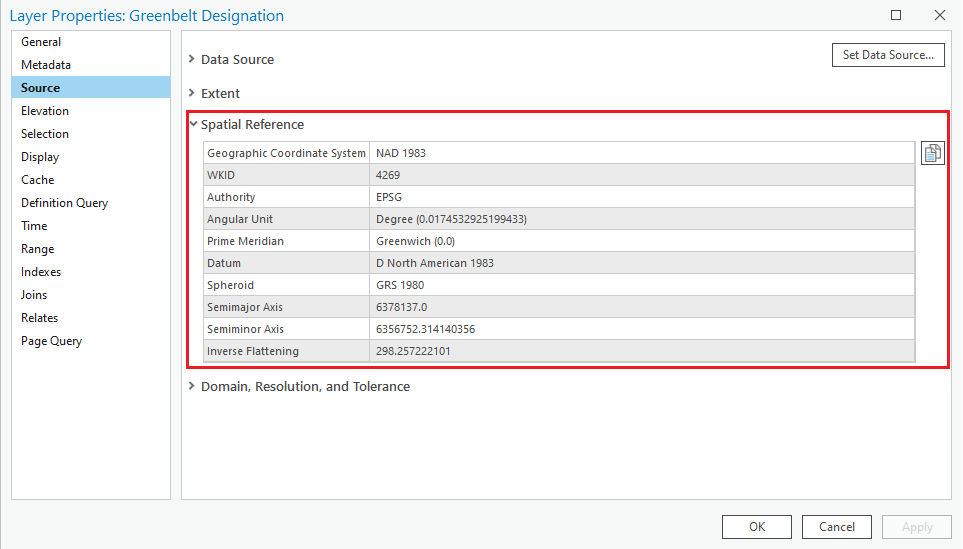
You can find out what coordinate system each layer is associated with by right-clicking on the layer name in the Contents pane, selecting Properties… and clicking on the Source tab in the Layer Properties window.
-
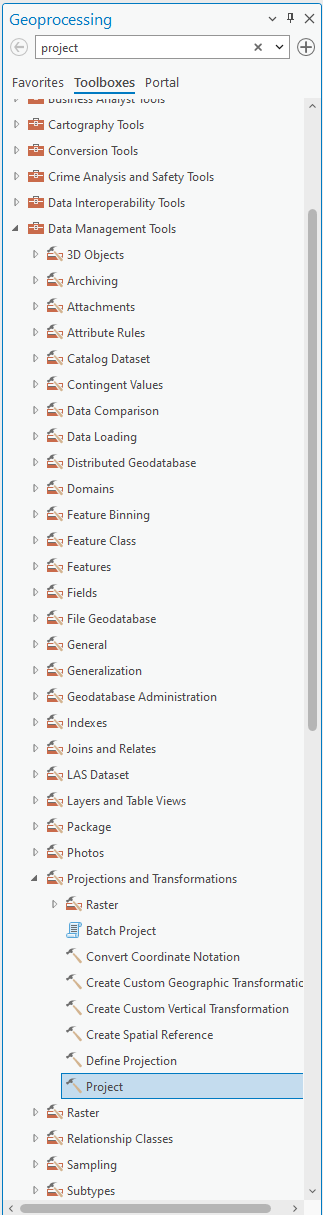
To project your layers, open the ArcToolbox window by clicking on the red toolbox found in the Analysis tab. Expand Data Management Tools, then Projections and Transformations. To project vector datasets double-click on Project. For raster datasets, expand Raster then double-click on Project Raster.

-
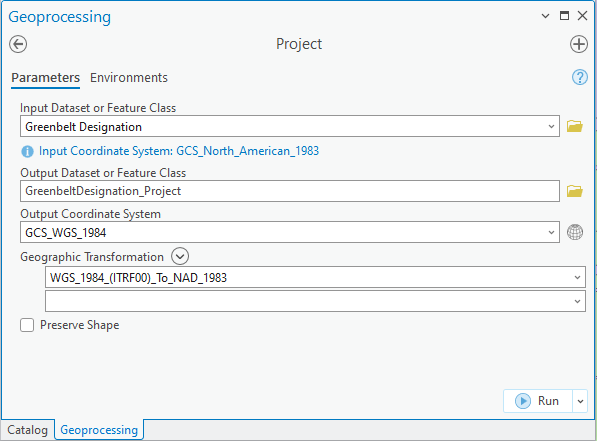
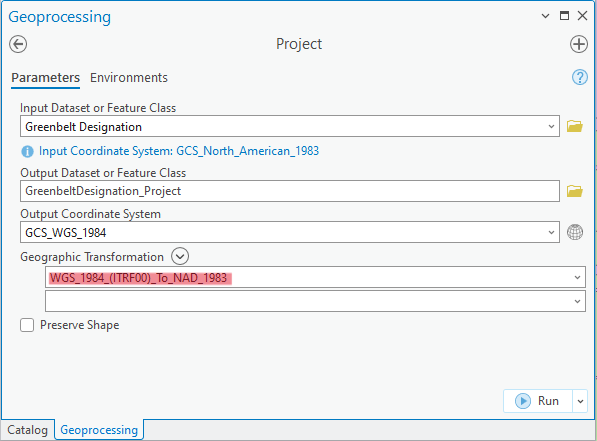
In the Input Dataset or Feature Class box (labeled Input Raster in the Project Raster tool), use the dropdown menu to select the dataset you are looking to project. (If it has not yet been loaded into the map document, click on the folder icon to browse to the appropriate folder and select it.)
The software should auto-detect the coordinate system of this dataset and will list it as Input Coordinate System.In the Output Dataset or Feature Class/Output Raster box, browse to the location where you would like to save the projected dataset and specify the filename. It is a good idea to indicate that these are the projected versions of other datasets, e.g. by adding “_projected” to the end of each filename.
Click the icon next to the Output Coordinate System box to select the projection that you would like to assign to the dataset. (Tip: if another one of your layers already has the correct projection selected, you can use the Import tool to find the right projection faster.) If the transformation involves a change in datum, you will be prompted to select a geographic transformation in the following box – a list of applicable transformations will be found in the Geographic Transformation dropdown menu. Click OK to project your dataset. When all your datasets are projected, you should begin a new map document (or manually change the coordinate system of the data frame to match your datasets) before conducting any spatial analysis.
-
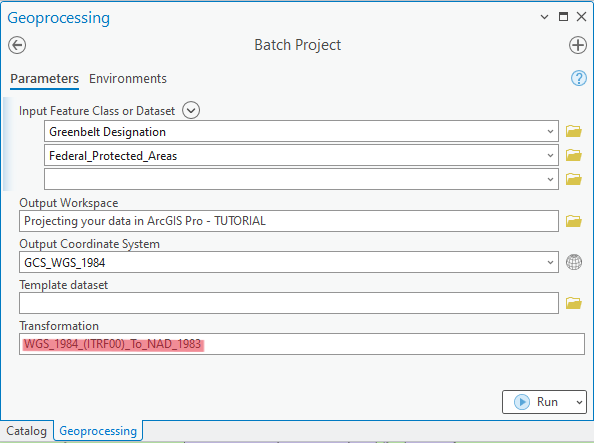
For advanced users: Are you looking to project a number of vector datasets at once? You can use the Batch Project function (located within ArcToolbox > Data Management Tools > Projections and Transformations > Batch Project) to project several at the same time. However, you may need to run the function multiple times, one for each group of input datasets that share a particular datum.
e.g. all datasets going from GCS_North_American_1983 to NAD_1983_UTM_Zone_17N will need to be done as one batch, all datasets going from GCS_WGS_1984 to NAD_1983_UTM_Zone_17N as another batch…
Before beginning the Batch Project process, you will need to note the appropriate geographic transformation to use for each set of datum shifts. You can do that by opening up the Project tool again, selecting an input dataset and the output coordinate system, and taking note of the recommended geographic transformations that appear in the dropdown menu. You’ll need to write down the exact name of the geographic transformation applicable to each group of datasets that you will be projecting – note that if you are projecting into a coordinate system that uses the same datum as the input datasets, no geographic transformation is required (such as the GCS_North_American_1983 to NAD_1983_UTM_Zone_17N example mentioned above).
The Batch Project tool works much in the same way as the Project tool outlined in this tutorial, except the Geographic Transformation needs to be typed into the Transformation box, instead of selected from a dropdown list of potential options.
Projecting your data in ArcGIS Pro
In order for many GIS functions to work properly, your datasets need to be stored in a common projected coordinate system. This guide will assist you with the projection process in ArcGIS Pro. (Unsure of what the appropriate projection is for your area of interest? Refer to this help document or ask a staff member for assistance in helping you determine it.)
Date Created:
Updated: